Pure Binding Power for Reliable Biotech Applications

Avidin: How to be Innovative with a Binding Protein
e-Proteins is the only native avidin producer and avidin supplier achieving 100% purity. As a result, this high quality becomes crucial when avidin is applied across different applications requiring optimal binding performance.
For instance, you may want to increase purification capacity, enhance detection signal, or reduce non-specific binding. In each case, product purity is the principal element. Therefore, this purity guarantees performance, reliability, and repeatability.
100% Avidin Purity: The Start of all Cutting Edge Derivatives and Conjugates
Avidin is basically an egg protein that has many different functions. Initially, in-vitro diagnosis kits used it, but now other fields such as cell culture are also using it. Avidin helps neutralize biotins and improves the purification process on a chromatography column. The improvement of the Avidin production process allows it to retain 100% purity level successfully.
Avidin has attracted interest from universities and research organizations. For several years, they have explored in-vivo diagnosis methods. These include cancerous cell targeting and drug delivery systems.
e-Proteins , as avidin producer, develops innovative avidin derivatives. These derivatives enhance cancerous cell targeting. They minimize unwanted binding with healthy cells.
This new derivative plays two roles: (i) it targets cancerous cells, and (ii) it serves as a carrier for the active components of drugs having cancerous cells. This double function allows complete coherence and continuity between the diagnosis and the cure.
Molecular Weight
With 99,9% of purety , the e-proteins product fits for all applications including the pharmaceutacl applicaiton
Avidin is a 66-KDa glycoprotein, produces in a hen’s oviduct and deposited in its egg albumen. Avidin’s molecular weight may differ slightly depending on the details in the literature.
Avidin – Biotin System
This egg protein, binds the water-soluble vitamin biotin (vitamin B7 or H) very tightly and with an outstanding dissociation constant of ~10-15 M. Once formed, the bond between biotin and Avidin rapidly forms, remains unaffected by extremes of temperature, organic solvents, other denaturing agents, and pH.
The stability and affinity of the protein for biotin have also been extensively investigated and characterized. It folds into a quaternary tetramer structure of 4 identical amino acid compositions and sequence subunits containing 9 lysine residues.
Researchers extensively use the avidin-biotin system as a mediator in various biological applications. These applications include isolation, localization, cytochemistry, immunoassay, and diagnostics.
However, avidin isolated from egg white has certain limitations. Specifically, its alkaline properties and oligosaccharide content appear responsible for non-specific interactions at biological levels. As a result, researchers originally preferred using the bacterial biotin-binding analog, Streptavidin, instead.
As avidin supplier , our bioengineers have corrected avidin’s non-specific absorption properties. They developed a neutral and deglycosylated form called NeutraLite Avidin or Neutralite Avidin.
This conjugate exhibits very low non-specific absorption. It preserves many lysine residues for chemical derivatization. This enables flexible conjugation strategies.
How Avidin Binds the Biotin?
The biotin-binding site is a deep, pear-shaped pocket. Specifically, its volume, three-dimensional structure, and residue orientation are predetermined as complementary to the incoming vitamin. Notably, in the absence of biotin, the binding pocket contains five water molecules. These water molecules mimic the biotin (vitamin B7) structure in the binding site until biotin arrives.
Initially, in the apo-protein (without ligand), the vitamin-binding pocket is fairly open due to the flexible L3,4-loop. Consequently, this flexibility allows fast access of biotin to the binding site.
Subsequently, the β-barrel structured protein binds and buries biotin inside its central pocket, with the vitamin’s bicyclic ring located at the bottom of the cavity. During this process, conformational readjustments of the protein occur, mainly involving the stiffened L3,4-loop, but also L5,6. These readjustments trap the vitamin. Simultaneously, three amino acid residues of L3,4 contribute additional interactions with biotin. Therefore, the extremely slow dissociation rate of biotin from Avidin arises from its high affinity for the protein.
How can Biotin Significantly Interfere with Lab Test ?
Identifying samples that already contain biotin technology can be difficult for assays using the biotin technology based on avidin. Indeed, patients taking biotin as a supplement could present high levels of biotins in their specimens. So, if the patient takes up to 300 mg per day of biotin (Vitamin B7), the concentration of biotin in their specimens can reach 1200ng/mL.
This presence of biotin in the specimens can cause significant interference with the lab test or with the diagnostic tests using the biotin technology such as avidin.
For the time being, the main criteria to define is whether the test can be affected by the biotin in the specimens based on the biotin concentration. This biotin level is set to 1200ng/mL.
FDA is investigating with all stakeholders to understand the interference of the biotin in the specimens with the test lab or diagnostics tests using the biotin technology.
What is the Avidin Market ?
The egg protein has usage in diagnostic kits, cell cultures to block biotin and pharmaceutical. All of those markets have their certification and quality requirements. e-Proteins is able to reach all of those certifications, including the virus inactivation when required.
What is the Avidin Purification Process ?
e-Proteins bases its purification process on proven technology spanning over 30 years. Belovo Chemicals (Bastogne, Belgium) developed this technology in the 1990s as a world leader in egg technology.
In 2012, e-Proteins launched an R&D project. The company improved and optimized this process to deliver the highest quality to customers. Today, our product achieves >99% purity. We can produce it with an endotoxin-free certificate (batch size 50 gr).
Producing 1 kg of purified avidin requires 5 tons of albumen from 800,000 eggs.
In 25,000 kg (25 tons) of albumen from 800,000 eggs, 1.2 kg of Avidin is available for extraction at 100% yield. The current yield is about 30%, so a production batch is about 500 gr of freeze-dried product.
The purifiaction step needs a dedicated resin with advanced binding capacity
What is the Iso-Electric Point of Avidin?
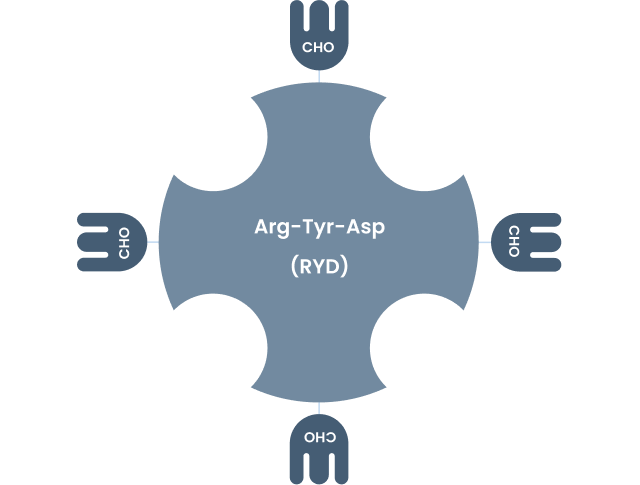
Avidin is highly cationic with an isoelectric point (pI) of about 10.5. Glycosylation occurs at the Asn-17 residue in a typical NXT(S) or Asn-Xxx-Thr(Ser) type carbohydrate-containing consensus sequence. Oligosaccharide components (heterogeneous structures composed largely of mannose (Man) and N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNac)) and positively charged amino acid residues (Lys & Arg) can interact nonspecifically with lectins and negatively charged cell surfaces and nucleic acids, thereby potentially causing nonspecific bindings in diagnostic and therapeutic applications1.
An avidin derivative enables us to avoid this non-specific bonding.
Bioengineering methods have been developed to suppress such nonspecific bindings. The result: NeutraLite Avidin, a nonspecific binding-free form of native protein, in which the signal/background ratio can be customarily adjusted (see Hookdin or Oligomerized neutralite avidin) and the biotin-specific binding can be made reversible (see Nitroavidin, Avidin Monomer, Iminobiotin) to accommodate an ever larger range of applications.